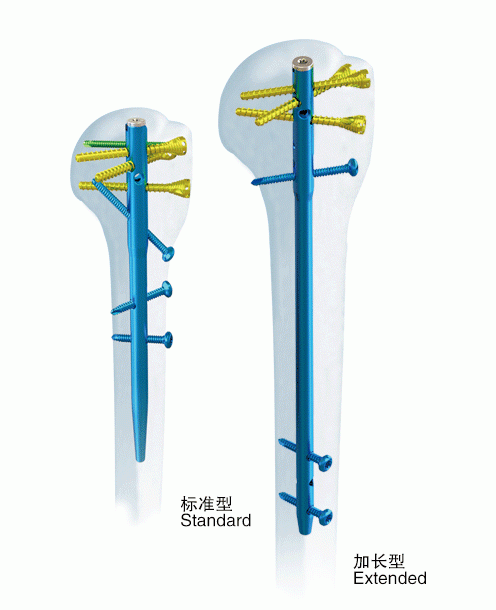
● Blunt screw tip to reduce the risk of secondary perforation
● 4 suture holes to enable reliable attachment of the rotator
● countersunk screw heads to reduce the risk of impingement
● Optional secondary 3.5 mm locking screw (screw-in-screw) for improved fixation in osteoporotic bone
● Straight nail design for central insertion point:
1.Improved anchorage in strong subchondral bone
2.Potentially avoiding insertion through fracture site in typically 3-part fractures
● Proximal locking holes can provide angular stability and reduce instances of screw back-out.
● Ascending screw option to provide support to the calcar.
● Multiplanar distal locking options for less implant toggling in the medullary canal.
Insert sutures (optional)
The stability of the osteosynthesis can be improved with the insertion of sutures. Place one or more heavy
nonabsorbable sutures in the region of the tendinous insertion of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis muscles
Attach the sutures to the MultiLoc Screw using the suture holes provided.
 Tel:
Tel: